Change of State of Matter
Change of State of Matter: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Vaporisation of Substances, Temperature Versus Time Graph for Heating of Ice, Fusion of Substances, Thermal Equilibrium During Change of State, Latent Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporisation, etc.
Important Questions on Change of State of Matter
Draw the temperature versus time graph for heating of ice.
Perspiration cools our body through evaporation.
Water kept in an earthen pot remains cool even in summers is an application of evaporation.
What is evaporation? Explain any one application of evaporation.
Explain any three applications of evaporation.
Two systems are in thermal equilibrium. The quantity which is common for them is
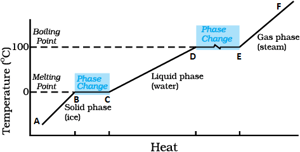
Identify the part representing latent heat of vaporization in the temperature vs heat graph for melting of ice.
The amount of heat energy absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase is called the specific latent heat of _____.
The change of state from liquid to vapour is called _____.
How the internal energy of a body changes during the process of fusion?
During the process of fusion:
In the temperature-time graph of heating of ice, the portions parallel to the time axis represents:
In the temperature-time graph of heating of ice, the melting point of ice is:
Temperature versus time graph for heating of ice:
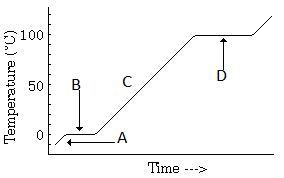
The part of the graph, which shows the thermal equilibrium of ice and water is represented by:
Conversion of liquid into vapours is called _____.
Change of water into ice, on freezing.
Hint: This state of matter has definite shape and volume.
